The Keto Diet has become one of the most talked-about weight loss methods, gaining popularity through social media influencers and celebrities. Its focus on high-fat, low-carb foods has made it stand out in the crowded world of dieting. Many people swear by its effectiveness in shedding unwanted pounds, adding to its growing fan base.
However, the diet also faces criticism from health professionals and fitness experts. Its high-fat approach can be controversial, with concerns about its long-term effects on heart health and overall well-being. Some argue that the restrictive nature of the diet might make it difficult for people to maintain over time.
Despite the mixed opinions, the Keto Diet continues to be a popular choice for many looking to lose weight. It has sparked a wide range of discussions about fat consumption and its role in weight management, with supporters and critics alike weighing in on its benefits and drawbacks.
The Concept of Ketosis
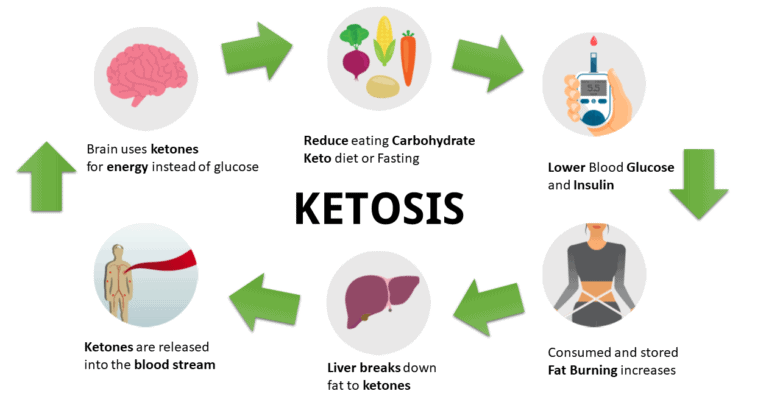
When you drastically reduce your carbohydrate intake, your body is no longer able to use glucose (sugar) as its primary source of energy. Glucose is the usual fuel for your body, but without enough carbs, the liver steps in and begins to break down fats into molecules known as ketones. These ketones become the new main energy source for the body. This shift from using carbohydrates for fuel to burning fat is referred to as ketosis, and it is the foundation of the ketogenic diet.
To achieve and maintain ketosis, the keto diet focuses on specific macronutrient ratios. Typically, 70-80% of the diet comes from fats, while 15-20% comes from proteins, and only 5-10% is made up of carbohydrates. This low-carb approach forces the body to turn to fat stores for energy. By limiting carbs so drastically, your body has no choice but to switch its energy source from sugar to fat.
The reason so many people turn to the keto diet for weight loss is this very process of burning fat for fuel. Once in ketosis, the body becomes much more efficient at breaking down stored fat to use for energy, which can result in weight loss over time. This fat-burning shift can help reduce body fat percentage and may lead to a leaner physique. It’s the transition from carb-burning to fat-burning that makes the keto diet so effective for those looking to shed excess weight.
How Does the Keto Diet Promote Weight Loss ?
1. Increased Fat Burning
As mentioned earlier, the ketogenic diet promotes burning fat instead of carbohydrates for energy. This process, called ketosis, helps with weight loss in a couple of ways. First, your body becomes more efficient at using fat as fuel, leading to fat loss. Second, ketosis may reduce appetite, as ketones produced during fat breakdown can help regulate hunger hormones, making you feel less hungry and potentially leading to fewer cravings. This combination supports effective weight loss.
Fat as Fuel: On the ketogenic diet, a large portion of your daily intake comes from fats, which prompts your body to adapt and become highly efficient at burning fat for energy. Since your body shifts from relying on carbohydrates to using fat as its primary fuel source, it becomes more adept at breaking down stored fat and converting it into usable energy. This increased fat-burning process helps reduce body fat over time, contributing to overall weight loss.
Decreased Appetite: The ketogenic diet may also help reduce your appetite, making it easier to manage food intake. Some studies suggest that the ketones produced during the breakdown of fat help regulate hormones that control hunger, such as ghrelin and leptin. These hormonal changes may lead to a decreased desire to eat, resulting in fewer cravings and a more controlled appetite. As a result, you may find it easier to stick to a calorie-controlled diet without constantly feeling hungry.
2. Improved Insulin Sensitivity

One of the main contributors to weight gain and obesity is insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This leads to higher blood sugar levels, which in turn encourages the body to store more fat. When insulin resistance occurs, the body’s ability to process glucose efficiently is impaired, making it harder to manage weight and leading to increased fat accumulation.
The ketogenic diet can help address this issue by significantly reducing carbohydrate intake. When carbohydrates are lowered, the body’s insulin levels drop, allowing cells to become more responsive to insulin. This improvement in insulin sensitivity helps the body better regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the likelihood of fat storage. As a result, the ketogenic diet can help promote weight loss by improving the body’s ability to manage glucose and fat. Over time, this can lead to reduced fat accumulation and more effective weight management.
3. Increased Thermogenesis
Thermogenesis is the process by which the body generates heat, playing a crucial role in weight loss by increasing the number of calories burned. It helps the body burn more energy, even when at rest, contributing to fat loss. Studies have shown that the ketogenic diet can stimulate thermogenesis by shifting the body from using carbohydrates to burning fat for fuel. This change leads to a more efficient calorie-burning process, which can further support weight loss.
As the body adapts to a state of ketosis, it becomes better at burning stored fat, and the enhanced thermogenesis helps accelerate this fat-burning process. This increased calorie expenditure not only aids in fat loss but also boosts overall metabolic efficiency. By improving thermogenesis, the keto diet allows individuals to burn more calories throughout the day, supporting long-term weight management and a more effective metabolic rate.
4. Lowered Carb Consumption
On a standard diet, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which serves as a quick and easily accessible source of energy for the body. However, if this glucose is not used immediately for energy, it can be stored as fat, potentially contributing to weight gain over time. This cycle can make it challenging for the body to burn fat efficiently, especially if a person consumes more carbs than their body needs for energy.
In contrast, the ketogenic diet limits carbohydrate intake significantly, which forces the body to shift its energy source from glucose to fat. Without the abundance of carbs to rely on, the body begins to break down fat into ketones, which it then uses for fuel. This shift not only helps reduce fat storage but can also lower overall calorie intake, as fats are more satisfying and tend to keep hunger at bay longer than carbohydrates. As a result, the keto diet may help create a calorie deficit and support fat loss more effectively.
Potential Benefits of the Keto Diet Beyond Weight Loss

While the keto diet is primarily popular for its weight loss effects, it may offer additional health benefits. These include:
Better Mental Clarity and Focus: Many individuals who follow the ketogenic diet report experiencing greater mental clarity and improved focus. When the body burns fat for energy, it produces ketones, which are believed to have neuroprotective properties. These ketones may support brain function by providing a steady and reliable source of energy for the brain. As a result, individuals on the keto diet often find it easier to concentrate, think more clearly, and maintain mental sharpness throughout the day. This enhanced cognitive function can improve productivity and mental performance.
Enhanced Physical Performance: While some athletes may initially be concerned that a low-carb diet could negatively impact their physical performance, research suggests that ketosis can be particularly beneficial for endurance athletes. By shifting the body’s primary energy source from carbohydrates to fat, the body gains access to a more abundant and long-lasting fuel supply. Unlike glycogen, which is stored carbohydrates and gets depleted quickly during intense activity, fat provides a steady and sustainable energy source. This can help improve endurance, allowing athletes to perform better during prolonged physical exertion.
Better Blood Sugar Control for Diabetics: For individuals with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing it, the ketogenic diet may offer significant benefits in terms of blood sugar regulation. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake, the keto diet helps lower insulin levels and reduce blood sugar spikes. This leads to more stable glucose levels throughout the day. For many people with diabetes, this improved insulin sensitivity can be a key factor in better overall blood sugar management. However, it’s important for individuals with diabetes to consult with a healthcare provider before starting the keto diet, as it may require adjustments to medication.
Potential for Improved Heart Health: The ketogenic diet may offer several potential benefits for heart health by improving various cardiovascular markers. Some research suggests that the high intake of healthy fats, such as those from avocados, olive oil, and nuts, can help reduce blood pressure, lower cholesterol levels, and decrease triglyceride levels in certain individuals. These changes can lead to a lower risk of heart disease. While the positive effects on heart health are promising, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term impact of the keto diet on cardiovascular health.
Risks and Considerations of the Keto Diet
While the ketogenic diet can offer various health benefits, it’s important to note that it may not be suitable for everyone. There are several risks and challenges associated with this diet, particularly in the long term.
Nutrient Deficiencies: One of the potential downsides of the ketogenic diet is the risk of nutrient deficiencies, particularly if followed for an extended period. Since the keto diet eliminates many foods that are rich in essential vitamins and minerals, such as fruits, whole grains, and legumes, individuals may miss out on key nutrients like fiber, potassium, magnesium, and vitamins A and C. These deficiencies can affect overall health, leading to issues like constipation, weakened immune function, or fatigue. To prevent this, it’s crucial to carefully plan meals to include a variety of nutrient-dense foods and consider supplements if you plan on following the keto diet long-term.

Keto Flu: When starting the ketogenic diet, many people experience a set of symptoms known as the “keto flu.” These symptoms, which can include headaches, fatigue, nausea, dizziness, irritability, and difficulty sleeping, are common as the body adapts from using carbohydrates to burning fat for energy. The transition can be challenging, but the symptoms are usually temporary, lasting anywhere from a few days to a week. Staying hydrated, replenishing electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium, and gradually easing into the diet can help minimize the discomfort and ease the adjustment process.
Risk of Increased Cholesterol Levels: While the keto diet has been shown to reduce triglycerides and increase good cholesterol (HDL) in some individuals, it can also potentially raise bad cholesterol (LDL) levels, especially due to the high intake of saturated fats. This is a concern for individuals with a history of high cholesterol or heart disease, as elevated LDL levels can increase the risk of heart disease. If you are following the keto diet, it’s important to regularly monitor cholesterol levels and consult with a healthcare provider to ensure your heart health remains in check.
Difficulty Sustaining Long-Term: The ketogenic diet is highly restrictive, particularly in terms of carbohydrate intake, which can make it difficult to maintain over the long term. Many people find it challenging to consistently follow such a strict eating plan, especially when it comes to social gatherings, dining out, or traveling. The inability to enjoy a wide variety of foods can lead to feelings of frustration, making it harder to stick to the diet. For many, the difficulty in sustaining the diet long-term often leads to weight regain once they revert to their previous eating habits, making it essential to carefully consider whether the keto diet is a sustainable choice for your lifestyle.
Risk of Eating Disorders: The restrictive nature of the keto diet may contribute to unhealthy relationships with food, especially for individuals who are prone to eating disorders. The constant focus on counting macronutrients, monitoring fat intake, and cutting out entire food groups can create anxiety or guilt around eating, potentially leading to disordered eating patterns. This heightened focus on food restrictions can negatively impact mental health, causing stress or feelings of failure if someone does not stick to the diet perfectly. For some, this could lead to a dangerous cycle of restrictive eating and bingeing, which can harm overall well-being.
Can the Keto Diet Help You Lose Weight? The Verdict
The ketogenic diet has certainly shown promise as an effective tool for weight loss, particularly in the short term. By encouraging the body to burn fat for fuel, suppressing appetite, and improving insulin sensitivity, many individuals have successfully lost weight while following the keto diet.
However, it’s important to note that the keto diet is not a one-size-fits-all solution. While it can be effective for some, it may not be suitable or sustainable for others. Nutritional imbalances, the difficulty of sticking with the diet, and the potential risks for certain individuals must be carefully considered.
Things to Keep in Mind:
Consult with a healthcare professional: Before starting any restrictive diet like keto, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Focus on whole, healthy foods: To maximize the benefits of the keto diet, focus on consuming nutrient-dense, high-quality fats, proteins, and low-carb vegetables.
Sustainability is key: Choose a weight loss approach that fits your lifestyle and is sustainable in the long term. The best diet for weight loss is the one you can maintain over time.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the ketogenic diet can be an effective weight loss strategy for some people by encouraging the body to enter ketosis, where it burns fat for energy. This shift from burning carbohydrates to fat can lead to fat loss and help individuals reach their weight loss goals.
However, it’s crucial to approach the keto diet with care, as it may not be suitable for everyone. It’s important to assess your individual health needs and long-term goals before committing to such a restrictive eating plan. A healthcare professional or nutritionist can offer valuable guidance to ensure the diet is a safe option for you.
If you choose to try the keto diet, take the time to research and plan your meals carefully. Proper meal planning ensures that you’re meeting your nutritional needs while working towards your weight loss objectives without sacrificing overall health.
FAQs
1. Is the Keto Diet Safe for Everyone ?
The keto diet is generally safe for most healthy adults, but those with certain health conditions (like liver disease or diabetes) should consult a doctor before starting.
2. How Long Does It Take to See Results on the Keto Diet ?
Results can vary, but many people start seeing weight loss within 1-2 weeks, especially as the body enters ketosis and begins burning fat.
3. Can I Exercise While on the Keto Diet ?
Yes, but you may experience reduced performance in the beginning, particularly for high-intensity exercises, as your body adapts to burning fat for fuel.
4. Will the Keto Diet Cause Nutrient Deficiencies ?
There’s a risk of nutrient deficiencies due to limited food groups. Eating nutrient-dense, low-carb foods and considering supplements can help address this.
5. Can You Stay on the Keto Diet Long-Term ?
It’s challenging for many people to maintain the keto diet long-term due to its restrictive nature, but it’s possible with careful planning and occasional breaks.



